Healthcare technology has always been about extending human capability, from the stethoscope amplifying what doctors could hear to X-rays revealing what the human eye couldn’t see. Autonomous AI agents, as they stand today, represent the next leap – tools that not only augment, but anticipate, coordinate, and act on their own to improve healthcare services and patient experiences.
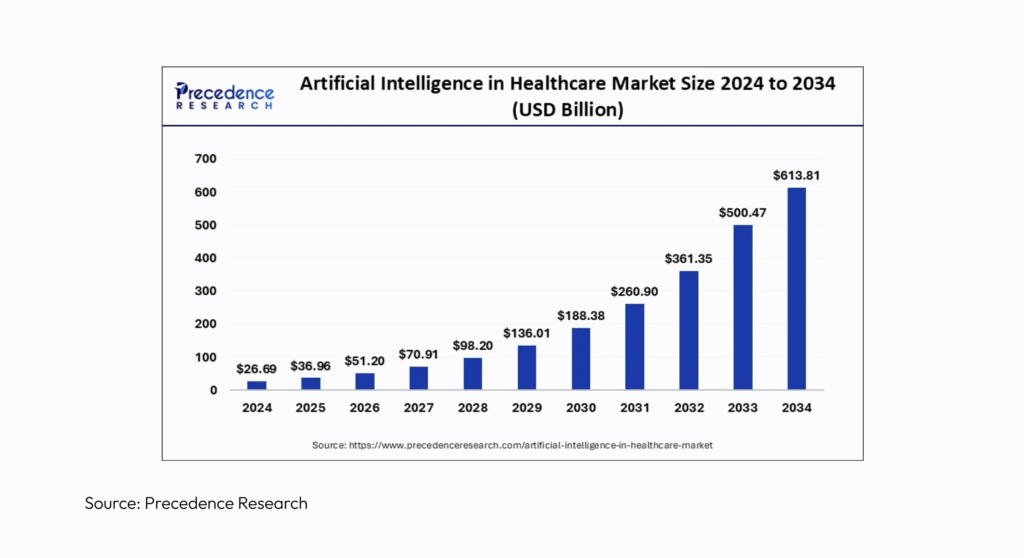
AI agents are advancing to think beyond appointment reminders and easy queries. Today, every major player in the market believes that the integration of AI into their workflows is mandatory, if not optional. This is especially true in healthcare as the market is projected to reach $868 billion by 2030, yielding $646 billion in cost savings and $222 billion in revenue gains. [1]
Figure 1: Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare Market Size 2024 to 2034
AI agents seamlessly replace traditional, single-function automation tools by demonstrating the ability to perceive, analyze, and act autonomously while maintaining human oversight. They seamlessly integrate with existing systems and ensure Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and European Health Data Space (EHDS) compliance. They are designed to leverage state–of-the-art, HIPAA-compliant, multimodal AI capabilities to interact with patients in natural, human language, making every conversation empathetic. These advanced autonomous AI agents are creating a new patient-centric healthcare industry.
Understanding Autonomous Healthcare AI Agents
Consider a well-trained, qualified nurse coordinator in a hospital who remembers every patient’s medication preferences, anticipates complications, and seamlessly coordinates with other departments to provide the best care. What if she had a digital assistant? One that could take some of her administrative burden so she could focus solely on what matters: patient care.
That’s autonomous AI agents. They go beyond rule-based automation to intelligent systems capable of complex decision-making and adaptive reasoning.
Let’s talk about its architecture: Natural Language Processing (NLP) allows agents to comprehend and respond to complex patient queries in multiple languages. Machine learning algorithms enhance performance through real-world interactions. Another notable feature is the multimodal AI capabilities, which make this technology accessible to all patients alike. Seamless Electronic Health Record (EHR) integration through Health Level 7 (HL7) and Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) standards confirms real-time access to patient data while maintaining enterprise-grade security protocols.
The true differentiating factor of autonomous agents is their capability to span an entire patient’s journey — from first contact to aftercare. They have the ability to perform remote patient monitoring and chronic disease management, triage symptoms, appointment scheduling, and medication compliance while retaining contextual knowledge of previous interactions and patient-specific preferences. This makes them excellent digital care coordinators that amplify clinical care rather than replace clinical judgment.
Table 1: Traditional AI vs AI Agents in Healthcare
| Capabilities | Traditional AI | AI Agents |
| Decision Making | Rule-based responses following predetermined scripts and decision trees | Reasoning that perceives context, processes complex information, and takes purposeful action based on clinical protocols |
| Learning & Adaptation | Static performance with manual updates required for new scenarios | Continuous learning through machine learning algorithms that improve performance based on real-world patient interactions |
| Integration & Data Access | Limited connectivity requiring manual data entry and siloed operations | Seamless EHR integration via HL7/FHIR standards with real-time patient data access while maintaining enterprise security |
| Workflow Scope | Handles isolated tasks with handoffs between different systems | Orchestrate entire patient journeys from initial contact through follow-up care, maintaining contextual awareness across all touchpoints |
OneReach.ai Generative Studio X (GSX) Agent Platform enables healthcare organizations to use AI Agents for workflow automation and knowledge management. With the GSX Agent Platform, users can manage the entire agent lifecycle, starting from design, training, and testing to deployment, monitoring, and optimization of intelligent multimodal agents.
The Need for Autonomous AI Agents in Healthcare
Let’s look at the numbers. A recent healthcare survey by Deloitte revealed that more than 70% of C-suite executives across five countries identified improving operational efficiencies and productivity as their top priority for 2025. [2] The healthcare systems worldwide are caught in a storm of challenges. Constrained budgets, persistent staff shortages, relentless clinician burnout, and mounting pressure to implement new technologies — all while racing to meet rapidly evolving consumer expectations. The administrative overflow not only drives costs up but also leads to physicians’ burnout and reduced patient satisfaction.
The COVID-19-induced pandemic brought another wave of patient care expectations — 24/7 access, multilingual support, and digital-first experiences. AI agents are changing the way the healthcare sector operates entirely and delivering significant value.
Take Memorial Hospital at Gulfport, for example, which implemented voice AI patient scheduling and generated nearly $804,000 in additional revenue within seven months by reducing no-shows by 28%. [3]
In fact, a survey by McKinsey found that 85% of healthcare leaders from payers, health systems, healthcare services, and technology groups are either exploring or have already adopted AI in their organizations. The survey also highlights that more respondents were already in the implementation stage than in the proof-of-concept stage, suggesting that organizations are successfully advancing their AI investments. [4] These data show that successful AI agent deployment can not only improve patient experience but also financial performance.
Core Capabilities of Healthcare AI Agents
From healthcare call centre automation, intelligent call centre triage, smart workflow, and AI-driven patient navigation, let’s look at what’s possible with AI agents.
Intelligent Voice & Multilingual Communication
The Advanced NLP capabilities can engage in natural multilingual conversations, interpreting complex medical terminology and patient concerns with contextual accuracy. It eliminates language hurdles for care and serves a more diverse client population while reducing the cognitive load on your clinical staff to focus on complex cases.
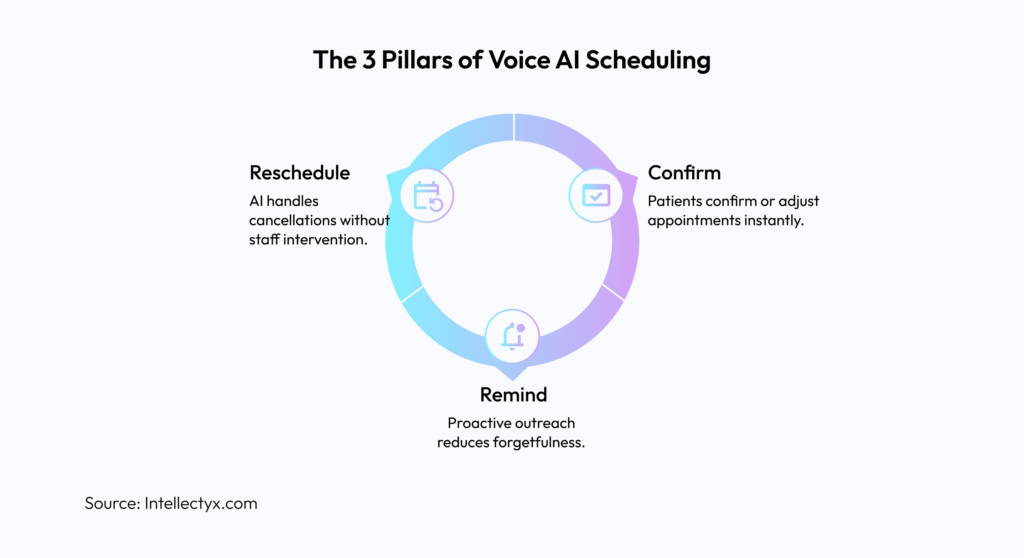
Figure 2: The 3 Pillars of Voice AI Scheduling
Real-Time EHR Integration & Clinical Context
Seamless integration through HL7 and FHIR standards provides real-time access to comprehensive patient information, including insurance details, medication history, drug interaction checks, and care coordination across multiple providers. This removes the information silos in healthcare experiences and also ensures that all interactions happen with full clinical context, improving safety and operational efficiency.
Predictive Analytics for Proactive Care
By analyzing past patterns, AI agents can anticipate patient needs and proactively take measures before problems emerge. For instance, they can predict appointment no-shows, identify patients at risk for emergency department (ED) visits, and even flag potential medication adherence issues. AI agents’ predictive capabilities can transform your approach from reactive firefighting to proactive care management.
Omnichannel Patient Engagement
It’s crucial to be where your patients are. These autonomous healthcare agents unify communications across voice, text, email, and video platforms, allowing patients to interact in their preferred channels while maintaining care continuity. The omnichannel approach provides extensive and thoughtful care. It also reduces the complexity of managing multiple communication channels, all of which require separate protocols and training requirements.
Clinical Decision Support with Safety Guardrails
Advanced AI agents are designed to assess the severity of patients’ symptoms and recommend appropriate levels of care and escalate urgent situations to human physicians. Recent research has shown that generative voice agents can achieve or even exceed medical advice accuracy rates of 99%, indicating significant potential for reliable clinical support. [5]
Digital Twin Technology for Personalized Medicine
Digital twin technology has emerged as a leader in the capabilities of AI agents. But what does it do and how does it help? By creating virtual replicas of patients, this technology allows agents to simulate different treatment scenarios, predict possible outcomes, and refine care plans accordingly. It gathers data from wearables (such as smartwatches and glucose monitors), genetic information, and lifestyle factors to effectively create these simulations. This innovative capability paves the way for truly personalized medicine on a large scale, while anticipating how patients’ bodies might react without actually putting them through it.
Figure 3: Graphical representation of the development of a digital twin

Looking to build a business case for implementing AI agents?
Download WhitepaperKey Use Cases: From Scheduling to Patient Support
Intelligent Scheduling & Appointment Management
One of the most significant impacts of AI agents in healthcare is appointment scheduling, affecting every patient interaction. Manual processes are prone to errors, resulting in double appointments and avoidable inefficiencies. These mistakes, however small, lead to frustrated patients and overwhelmed staff. Autonomous AI agents provide 24X7 scheduling support with real-time calendar integration and intelligent conflict resolutions that work efficiently even when your staff sleeps.
AI agents, in fact, go beyond simple appointment booking to provide comprehensive calendar management. They proactively contact patients with personalized reminders through their preferred channels and automatically offer alternative slots when patients cancel. These agents use complex algorithms that factor in provider schedules, patient history, and even weather patterns to optimize utilization. They also keep a track of last-minute cancellations and immediately contact the patients who need urgent care from waiting lists.
AI-Powered Call Center Operations
From routine inquiries and medical concerns to insurance information, healthcare call centres serve as a critical touchpoint between patients and healthcare systems. AI agents excel following predictable patterns to automate insurance verification, prescription refills and billing-related issues while accessing real-time data.
Then comes the intelligent triage capabilities that enable agents to assess the urgency of the call and route patients appropriately. The agents can evaluate symptoms and depending on the care patients need, they escalate the crucial cases to human clinicians.
Case study 1: A global healthcare service provider serving over 160,000 medical practices and 110 million patients faced massive traffic spikes and needed efficient communication at scale.

Clinical Documentation & Revenue Cycle
Clinical documentation consumes massive portions of physician time, and ambient AI is changing that by capturing, transcribing, and structuring clinical encounters in real-time.
Ambient AI scribes capture patient-provider conversations and automatically populate EHR fields, significantly reducing documentation time while improving accuracy. Meanwhile, claim processing automation verifies patient eligibility, checks authorization requirements, and identifies potential claim denials before submission, directly protecting revenue cycles.
The predictive analytics capabilities enhance claims processing by identifying patterns that indicate potential issues. Agents can flag unusual billing patterns, verify procedures, and ensure compliance with payers’ requirements. This intelligence protects healthcare organizations from any financial losses while also contributing to the overall healthcare cost containment.
Mental Health & Wellness
Providing mental health support is one of the rapidly growing applications of AI agents in healthcare. These specialized agents are addressing the supply shortage by providing 24X7 emotional support, conducting wellness check-ins, and delivering evidence-based interventions — all using NLP models explicitly trained for behavioral health data. They can recognize signs of emotional distress, provide cognitive behavioral therapy techniques, and offer coping strategies based on defined clinical protocols. They also have built-in escalation capabilities to redirect complex cases to human clinicians.
Integration with wearable devices can work as a strong safety net, keeping an eye on variations in heart rate, sleep patterns, and daily activity that might be signs of incoming mental health issues. When these indicators suggest someone might be struggling, agents can proactively reach out by sending a gentle check-in. This preemptive care isn’t possible with traditional models that wait for patients to reach out for help, which isn’t always reliable when it comes to mental health issues.
The perceived anonymity and depersonalization of the AI agent allow patients to feel free to open up to the AI agent in early sessions. While strict HIPAA compliance remains non-negotiable, this dynamic creates early intervention opportunities. Patients might share concerns with AI agents that they’d hesitate to discuss in traditional settings, allowing identification of issues and connection to human support before crises develop.
Implementation Roadmap for Autonomous Healthcare Agents
Rolling out autonomous AI agents isn’t something you do over a weekend. Smart healthcare organizations take a systematic approach that builds confidence while managing risk because getting this wrong affects patients who need care and real outcomes.
Start with a Strong Foundation: Before any AI agent touches patient data, organizations must have strong HIPAA compliance, comprehensive encryption, access controls, and audit trails. This phase is about getting your technical house in order: planning HL7 and FHIR integrations, establishing governance committees with clinical leaders and IT professionals, and most critically, educating your staff on what these agents can and cannot do. Change management isn’t optional here; your nurses and physicians need to understand they’re getting powerful allies, not replacements.
Build Core Capabilities: Start with appointment scheduling. It’s well-defined, high-volume, and patients immediately notice the improvement. Voice AI agents provide patients with the intuitive conversations they expect. Your Electronic Health Record (EHR) integration goes live with secure API connections, and call centers begin routing routine inquiries to agents. At the same time, human staff handle the complex, empathy-requiring cases. This is where your organization starts to see tangible results.
Scale Advanced Features: Now, AI agents tackle clinical documentation, patient triage, and chronic disease monitoring. Advanced machine learning models handle sophisticated interactions, and digital twin technology gets deployed for your highest-value patients. This phase separates early adopters from followers. Your organization is not just automating tasks; it is fundamentally improving care delivery.
Optimize and Measure: Performance measurement becomes critical at early stages. Advanced analytics show AI agent performance, patient satisfaction scores, and clinical outcomes. Organizations typically see a jump in return on investment (ROI) as agents handle increasingly complex responsibilities and demonstrate a measurable impact on key metrics.
The Human-in-the-Loop workflow enables continuous monitoring, allowing issues to be identified and addressed before they escalate. Once you get these fundamentals right, AI agents become a competitive advantage for every healthcare organization.
Table 2: AI Agent Implementation Roadmap
| Phase | Timeline | Key activities | Technologies |
| Foundation | Months 1-3 | HIPAA compliance setup, HL7/FHIR integration planning, Staff training, Pilot use case selection | HIPAA frameworks, Basic AI agents, Security protocols |
| Core implementation | Months 4-8 | Voice AI deployment, EHR integration, Appointment scheduling automation, Call center integration | Voice AI platforms, API integrations, and Workflow automation |
| Advanced Integration | Months 9-15 | Clinical documentation, Patient triage, Chronic disease monitoring, Predictive analytics | Advanced NLP, ML models, Digital twins, Predictive AI |
| Optimization | Months 16-24 | Performance optimization, Advanced analytics, Scale deployment, ROI measurement | Analytics platforms, Performance monitoring, Advanced AI models |
Measuring ROI and Patient Outcomes
To measure the ROI (Return on Investment) for healthcare AI agents, a comprehensive evaluation of both quantitative metrics and qualitative improvements in patient experience is required.
Healthcare systems that deploy AI for call center operations report daily savings that add up to millions of dollars annually. Administrative tasks that used to consume the majority of the staff’s time are now handled by agents, freeing clinical teams for actual patient care.
Smart rebooking algorithms maximize schedule utilization, ensuring patients actually get the appointments they need. Claims processing speeds up with fewer denials because AI agents catch issues before submission.
Patient satisfaction metrics demonstrate the qualitative benefits of AI agent deployment. Organizations implementing comprehensive AI agent programs report improved patient satisfaction scores due to enhanced accessibility, reduced wait times, and more personalized interactions. The 24×7 availability of AI agents particularly benefits patients who need after-hours support or have scheduling constraints.
More importantly, clinical outcomes improve. Early intervention capabilities through continuous monitoring reduce emergency department visits for chronic disease patients. AI-supported medication adherence programs show meaningful compliance improvements, directly impacting health outcomes while reducing costly complications that drain resources.
AI-supported clinical documentation cuts physician documentation time significantly, allowing providers to see more patients or spend additional time on direct care. Automated scheduling and patient communication free staff to handle complex cases that genuinely require human judgment and empathy.
Figure 4: Benefits of AI Agents in Healthcare
Challenges and Governance Considerations
Healthcare AI governance isn’t about managing technology; it’s about patient safety, where algorithms directly influence clinical decisions.
Algorithmic Bias: The Hidden Risk
AI models trained on incomplete datasets perpetuate healthcare disparities at scale. Leading organizations implement continuous bias monitoring with multidisciplinary audit teams. This isn’t simply compliance; it’s fundamental to equitable care and liability protection.
Safety as Competitive Advantage
Large language models generate convincing but dangerous misinformation. Industry leaders establish strict safety boundaries with mandatory human oversight for critical decisions, while explainable AI builds the trust necessary for adoption. Organizations mastering transparent AI decision-making will differentiate in an increasingly commoditized market.
Legacy Integration Reality
Most healthcare systems operate on a decades-old EHR infrastructure with limited interoperability. The question: Do modernization costs justify AI ROI, or do legacy limitations create competitive vulnerability demanding immediate action?
Proactive Regulatory Compliance
HIPAA is a baseline. Forward-thinking organizations stay ahead of evolving Food and Drug Administration (FDA) guidelines, state requirements, and federal AI frameworks through continuous legal review. Reactive approaches expose organizations to penalties and delays.
Enhanced Security Architecture
AI systems processing vast healthcare datasets require zero-trust architectures and AI-specific incident response protocols. Traditional cybersecurity frameworks are insufficient for AI’s unique attack vectors.
With greater autonomy comes greater responsibilities, and this couldn’t be truer in the healthcare sector. True transformation requires ethical and security considerations to ensure compliance and avoid unintended consequences.
Toward Patient-Centric, Autonomous Healthcare
We’re witnessing the emergence of truly patient-centric healthcare delivery. Autonomous AI agents are dismantling barriers that have frustrated patients and exhausted providers for decades, creating seamless 24/7 experiences that actually work.
The business case is undeniable: dramatic reductions in administrative overhead, improved patient satisfaction, and cost savings that flow directly to the bottom line. More importantly, these efficiency gains free clinical teams to focus on what matters, true patient care and human connection that technology like AI agents amplify rather than replace.
As we stand at this inflection point, the question is not whether autonomous AI agents will transform healthcare but whether your organization will lead by example. The organizations that act decisively today, implementing autonomous agents with appropriate safeguards and human oversight, will define the future of patient-centric healthcare delivery.
Experience a free AI agent prototype for your use case
Free prototypeRelated Questions About AI Agents in Healthcare
1. Will AI agents replace the human staff in call centers?
AI agents will augment rather than replace human healthcare workers, fundamentally changing roles rather than eliminating them. Research indicates that AI can handle a significant portion of routine inquiries, including appointment scheduling, prescription refills, and basic information requests. This automation frees human agents to focus on complex patient needs requiring empathy, clinical judgment, and nuanced problem-solving.
The transformation creates new job categories while evolving existing ones. Human agents become AI supervisors, exception handlers, and relationship managers for patients with complex needs. Healthcare organizations report improved job satisfaction as staff transition from repetitive tasks to meaningful patient interactions that leverage uniquely human capabilities.
2. How do AI agents integrate with EHRs using HL7 and FHIR standards?
HL7 and FHIR standards provide the technical foundation for seamless AI agent integration with Electronic Health Record systems. FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) uses modern RESTful APIs and JSON formatting to enable real-time data exchange, while HL7 provides structured messaging protocols for clinical data communication.
AI agents leverage these standards to access patient demographics, clinical histories, appointment schedules, and treatment plans in real-time. API-based integration ensures that agents operate with complete clinical context while maintaining strict security protocols and audit trails. Successful implementations require careful mapping of data elements and testing to ensure accuracy and reliability.
3. Are AI voice agents reliable for patient scheduling?
AI voice agents demonstrate high reliability in patient scheduling applications, with accuracy rates exceeding 99% in clinical safety evaluations. Real-world implementations demonstrate practical effectiveness in live healthcare environments, with successful automation of thousands of patient interactions.
Key reliability factors include robust training on healthcare-specific datasets, continuous learning from patient interactions, and failsafe mechanisms that escalate complex cases to human agents. Performance monitoring and quality assurance processes ensure that agents maintain high accuracy while continuously improving through machine learning algorithms.
4. What governance models ensure HIPAA compliance?
Comprehensive governance models for HIPAA-compliant AI agents require multi-layered security frameworks, strict access controls, and continuous monitoring. Technical safeguards include end-to-end encryption, secure API gateways, and audit logging of all patient data interactions.




